1. AGRICULTURE
AGRICULTURE Paper 1 433/1SECTION A (30 marks)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
1. State four reasons for applying phosphatic fertilizers during planting. (2 marks) ...............................................
2. Give four ways in which crop pests are classified. (2 marks)
..........................
3. State four advantages of landlordism and tenancy. (2 marks)
................
4. Differentiate between apiculture and aquaculture. (1 mark)
........................
5. State four factors that affect the quality of “farm-yard manure. (2 marks)
......................
6. Give four reasons why seed propagation is encouraged in crop production.(2 marks)
.....................
7. State four factors that can make a farmer choose a jembe for primary tillage.(2 marks) .......................
8. Give four factors that affect the quality of hay.(2 marks)
......................................
9. Name five entries that can be made on a cattle breeding record.(2½ marks)
................................
10. Give two reasons for testing soil.(1 mark)
.......................
11. Name three forms of horticulture practiced in Kenya.(1½ marks)
...........................
12. Give two reasons for constructing a shade over a nursery.(1 mark)
...........................
13. Name four appropriate sites for agroforestry trees.(2 marks)
............................
14. State four personal safety measures a farmer should consider when handling herbicides.(2 marks)
.......................
15. Give two reasons why a maize plant growing in a cabbage crop field may be treated as a weed.(1 mark)
.................................
16. Name four classes of weeds. (2 marks)
.......................
17. State four agricultural activities that may pollute water. (2 marks)
...............................
SECTION B (20 marks)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
18. A farmer applied a compound fertilizer 10:20:0 on a three hectares piece of land at a rate of 180kg N per hectare.
(a) Calculate the quantity of the compound fertilizer the farmer applied on the piece of land.(3 marks)
.............................
(b) What do the figures 10 and 20 stand for in the compound fertilizer? (2 marks)
.......................
19. The diagram below illustrates a nursery practice.
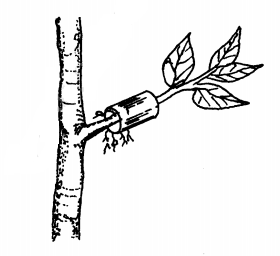
(b) Describe the procedure followed in carrying out the practice illustrated. (2 marks)
.......................
(c) State two advantages of the practice illustrated above in crop production. (2 marks)
.............................
20. The diagram below shows crop establishment using a certain method of planting.

(b) State two advantages of the planting method used for the crop. (2 marks)
..............................
(c) Explain two factors that determine the depth of planting. (2 marks)
..........................
21. Below is a diagram showing a crop disease.

(b) State three control measures for the crop disease. (3 marks)
.............................
(c) Name the category in which the crop disease is classified. (1 mark)
.................................
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided afler question 24.
22. (a)Explain how each of the properties of rainfall and light influence crop production.
(i) rainfall;(8 marks)
..................................
(ii) light.(4 marks)
..........................
(b)Describe rice production under the following sub-headings:
(i) land preparation;(2 marks)
..................................
(ii) water control;(2 marks)
.......................
(iii) fertilizer application;(2 marks)
.....................................
(iv) Weed control.(2 marks)
....................................
23. (a)Explain five factors that can increase the demand for tea on a market. (10 marks)
..........................
(b) State four ways of improving labour productivity on the farm. (4 marks)
...................................
(C) The following information was obtained from Upendo Farm inventory on 1st January 2013.
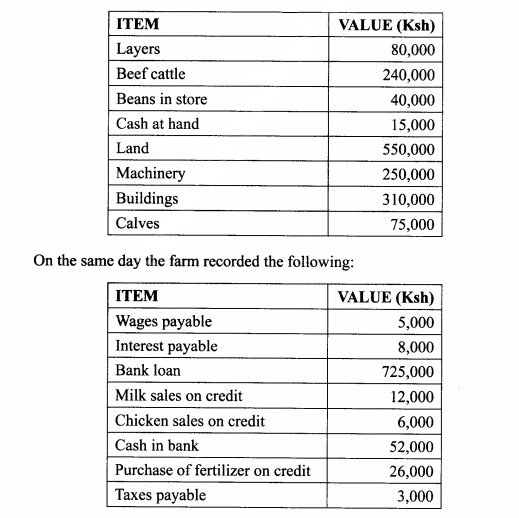
24. (a) Describe the field management practices for tomatoes. (12 marks)
.....................................
(b) Describe four types of soil erosion by water. (8 marks)
.......................................
AGRICULTURE
Paper 2 433/2
(THEORY)
1. Name four rabbit breeds reared in Kenya. (2 marks)
........................................
2. State four characteristics of desirable eggs for marketing. (2 marks)
............................
3. Name two types of roughage. (1 mark)
.............................
4. Give four disadvantages of inbreeding in livestock. (2 marks)
............................
5. Name the nutritional deficiency for each of the following livestock diseases:
(a) milk fever;(1/2 mark)
.........................
(b) bloat.(1/2 mark)
..........................
6. Give two reasons for docking in sheep rearing. (1 mark)
...................................
7. State four signs of fowl typhoid. (2 marks)
.................................
8. Differentiate between drift and pen lambing. (2 marks)
.....................................
9. State four features on the animal which may predispose it to livestock diseases. (2 marks)
..................................
10. Give four factors that affect milk composition. (2 marks)
...........................
11. State two control measures for keds in sheep. (1 mark)
............................
12. State two maintenance practices carried out on a greenhouse structure. (1 mark)
...........................
13. (a) Name the goat breed which is brown in colour with white strips running down the face to the nose. (½ mark)
..........................
(b) State four rearing practices that necessitate handling of piglets. (2 marks)
..........................
14. Give four preventive measures for livestock diseases. (2 marks)
.................................
15. State one function of each of the following parts during egg formation in poultry:
(a) funnel; (½ mark)
........................
(b) magnum;(½ mark)
..........................
(c) isthmus.(½ mark)
..........................
16. The following is a list of poultry breeds:
White Leghorn
Light Sussex
Rhode Island Red
Ancona.
Categorize them into:
(a) light breeds;(1 mark)
..........................
(b) heavy breeds.(1 mark)
..........................
17. State two functions of a queen in a bee colony.(1 mark)
..........................
18 State four maintenance practices carried out on a fish pond. (2 marks)
..........................
SECTION B (20 marks)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
19. The diagrams below represent some farm tools and equipment. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
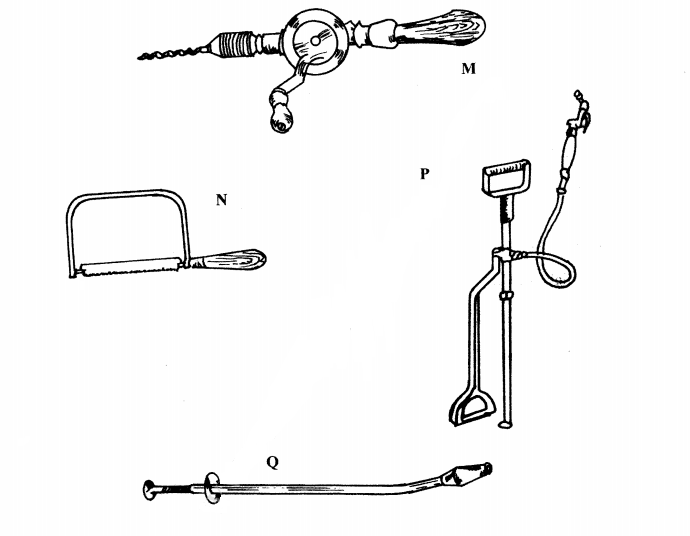
.............................
P (1 mark)
.............................
(b) State one use of each of the tools labelled M and Q.
M (1 mark)
....................
Q (1 mark)
....................
(c) Explain one maintenance practice carried out on the equipment labelled P. (1 mark)
............................
20. The diagram below represents parts of a roof.
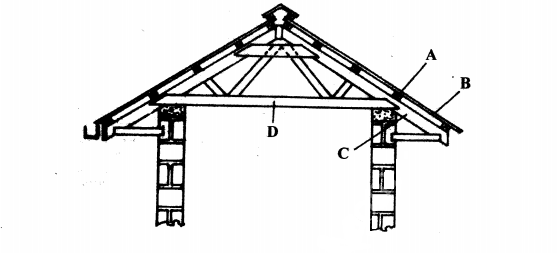
............................
C (1 mark)
............................
(b) State two types of materials that may be used for the part labelled D. (2 marks)
..........................
(c) Give one disadvantage of using thatch for the part labelled B. (1 mark)
.......................
21. The diagram below illustrates an internal parasite of livestock.

(b)Name two common species of the parasite illustrated above. (2 marks)
........................
(c)State two signs of worm infestation that may be observed in the dung of livestock (2 marks)
........................
22. Below is a diagram illustrating an instrument used in cattle breeding.
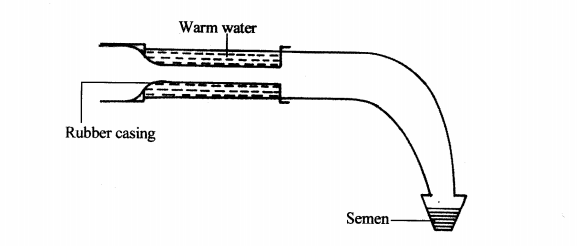
(b) State the role of the instrument in cattle breeding. (1 mark)
........................
(c) When would it be appropriate to serve a cow after the onset of heat? (1 mark)
........................
(d) Apart from the method in which the above instrument is used, name two other methods of serving a cow. (2 marks)
........................
SECTION C: (40 marks)
Answer any TWO questions from this section in the spaces provided after question 25.
23. (a) Give the functions of any five parts of a poultry egg. (10 marks)
........................
(b)Describe the uses of five materials/equipment required for hand milking. (10 marks)
........................
24. (a)Describe East Coast fever under the following sub-headings:
(i) livestock affected; (1 mark)
........................
(ii) vector and causal organism; (2 marks)
........................
(iii) signs of attack; (5 marks)
........................
(iv) control measures. (2 marks)
........................
(b)Describe the activities that take place during the digestion process in the rumen. (5 marks)
........................
(c)Describe the management practices that ensure proper hygiene in a deep litter poultry house. (5 marks)
........................
25. (a)State five signs of external parasite infestation in livestock. (5 marks)
........................
(b)Explain five factors that should be considered when siting a farm store. (5 marks)
........................
(c)Describe the cycle of a four stroke petrol engine. (10 marks)
2. BIOLOGY
231/1 BIOLOGY
Paper 1
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
1. (a) What is meant by the term binomial nomenclature? (1 mark)....................................
(b) State two guidelines that should be followed when typing scientific names.(2 marks)
..................................
2. During a lesson, students observed the structure of bat, cat and human forelimbs to determine their evolutionary relationship.
(a) State the name given to the structure of the limbs observed by the students(1 mark)
.................................
(b) Name the type of evolution illustrated by the structure of the limbs observed.(1 mark)
.......................................
(c) What evidence of evolution is illustrated by the limbs? (1 mark)
...................................
(d) State the significance of the type of evolution illustrated by the limbs. (l mark)
...................................
3. An individual is of blood group B positive.
(a) Name the antigens in the individuals blood. (2 marks)
....................................
(b) Give the reason why the individual cannot receive blood from a blood group A donor.(2 marks)
................................
4. Colour blindness is a sex linked trait controlled by a recessive gene b. If a mother is a carrier and the father is normal, What is the chance that their son will be colour blind? Show your working. (4 marks)
......................
5. (a) State two advantages of using a coverslip when preparing a specimen for observation under a light microscope. (2 marks)
.........................
(b) How is the low power objective lens manipulated to focus a specimen for observation under a light microscope? (2 marks)
................................
6. Students set up an experiment as illustrated below.
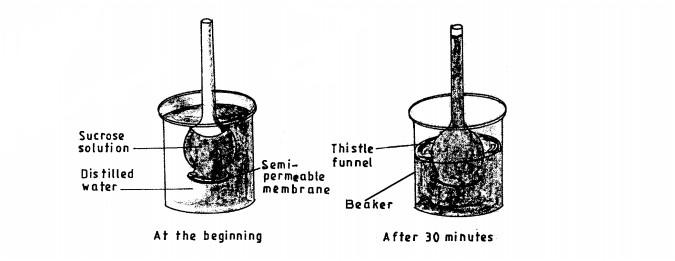
(b) State the importance of the physiological process investigated in plants. (1 mark)
.....................
(c) Explain the observations made after 30 minutes. (2 marks)
..............................
7. How is a guard cell structurally adapted for gaseous exchange? (4 marks)
........................
8. (a) Name the organism that: -
(i) causes malaria; (1 mark)
.........................
(ii) transmits malaria. (1 mark)
............................
(b) State two control measures for malaria. (2 marks)
...........................
9. The diagram below shows an experimental set up to investigate a certain physiological process in plants.
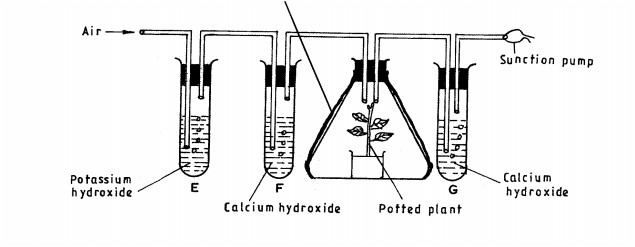
(b) State the role of the following in the experiment:
(i) potassium hydroxide; (1 mark)
............................
(ii)Aluminium foil.(1 mark)
..........................
(c) Account for the expected colour change in tube F.(2 marks)
..........................
10. The diagram below illustrates skulls of human adult and chimpazee.
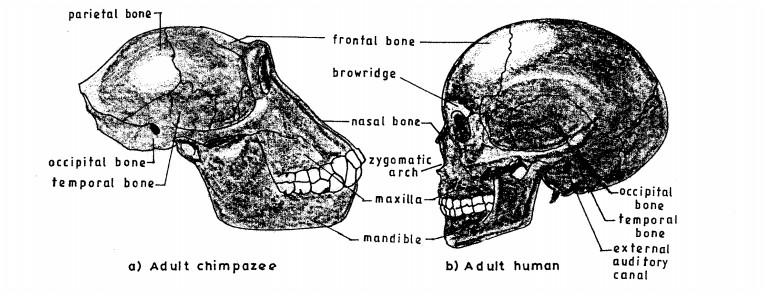
11. Name two structures used for gaseous exchange in plants. (2 marks)
........................
12. (a) What is meant by each of the following:
(i) pyramid of biomass? ( l mark)
......................
(ii) pyramid of numbers? (1 mark)
.........................
(b) During an ecological visit to the Savanna Grassland, students were able to see lions, antelopes, vultures and pastoralists grazing their cattle. Construct a food chain with four consumer levels to illustrate the energy flow in the ecosystem. (2 marks)
............................
13. State three differences between the end products of mitosis and meiosis.(3 marks)
........................................................
14. (a) Name two types of involuntary muscles in mammals. (2 marks)
...........................
(b) State the location of each of the muscles named in (a) above. (2 marks)
........................................
15. The photomicrographs below show the various stages of cell division in a certain plant.
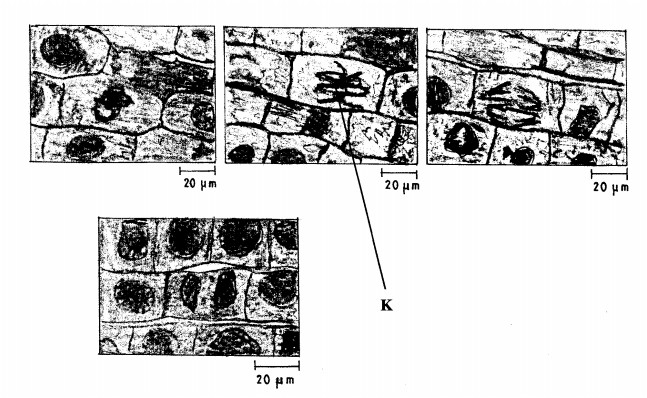
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (a) (i) above. (1 mark)
........................................
(b) (i) Name the stage of cell division labelled K. (1 mark)
............................
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above. (1 mark)
................................
16. State four structural differences between millipedes and centipedes. (4 marks)
.............................................
17. (a) How is a human stomach adapted to
(i) protein digestion? (2 marks)
.............................
(ii) churning? (2 marks)
.............................
(b) What happens to the glucose synthesized during photosynthesis? (2 marks)
...........................
18. The diagram below shows an experimental set-up to investigate the conditions necessary for germination. Test tube P was placed in a refrigerator while Q was left at room temperature. The set-ups were observed regularly for two weeks but no germination occurred.
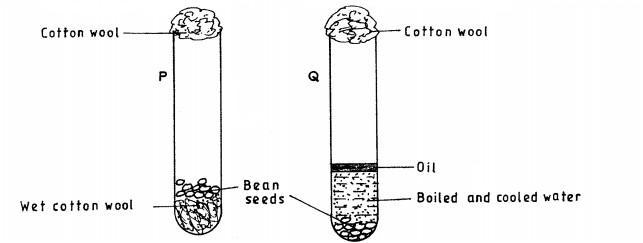
................................
Q (3 marks)
.................................
19. (a) Using the axes provided below, sketch a curve to illustrate the growth pattern observed in the phylum arthropoda. (2 marks)

20. Below are components of a simple reflex pathway:
.................................
BIOLOGY
Paper 2(Theory)

1. The diagram below illustrates a blood capillary surrounding a structure for gaseous exchange in human beings.
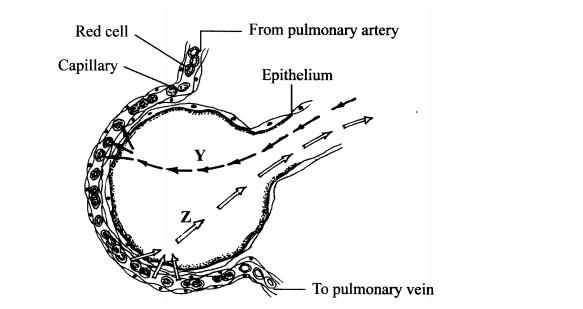
(b) Identify the gases labelled Y and Z.
Y.................................(1 mark)
Z..................................(1 mark)
(c) How does the gas labelled Y reach the inside of the blood capillary?(3 marks)
...................................
(d) How does cigarette smoking lead to lung cancer?(2 marks)
.................................
2. The diagram below illustrates the structure of the female part of a flower.
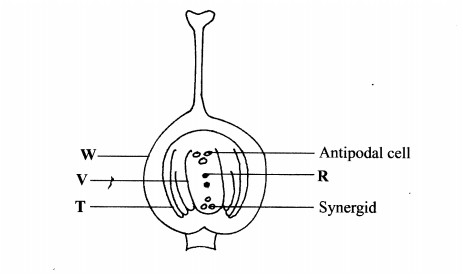
(b) Describe what happens when the pollen tube enters the structure labelled V. (5 marks)
.............................................
(c) What do the structures labelled R and T develop into after fertilization?
R.....................................(1 mark)
T.....................................(1 mark)
3. (a) What is meant by the term genetics? (1 mark)
...............................
(b) State two examples of discontinuous variation. (2 marks)
.......................................
(c) A female with sickle cell trait marries a normal man. The allele for sickle cell is Hbs and the normal allele is HbA. Deternine the probability that their first born will have the sickle cell trait. Show your working. (5 marks)
........................
4. In an experiment to investigate a factor affecting photosynthesis, a potted plant which had been kept in the dark overnight was treated as shown in the diagram below and exposed to light.
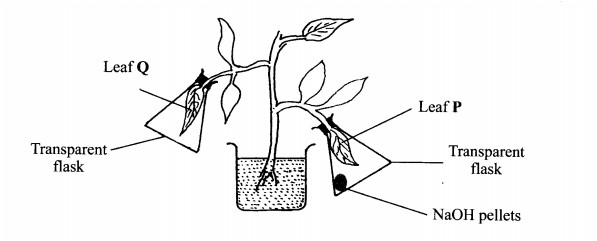
(b) Which factor was being investigated in the experiment? (1 mark)
...........................
(c) (i) Which test did the students perform to confirm photosynthesis in the leaves labelled P and Q? (1 mark)
.............................
(ii) State the results obtained in the leaves labelled P and Q.
P ........................ (1 mark)
Q......................... (1 mark)
(iii) Explain the results obtained in the leaves labelled P and Q.
P .........................(1 mark)
Q..........................(l mark)
(d) What was the purpose of leaf Q in the experiment? (1 mark)
...........................
5. In an experiment to investigate a plant response, the set up shown in the diagram below was used.
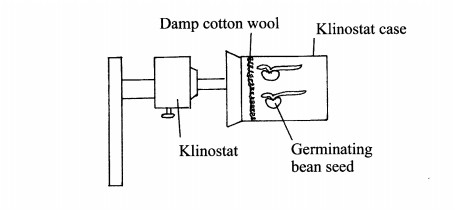
(b) If the Klinostat was not rotating:
(i) state the observations that would be made on the seedlings after three days; (2 marks)
................................
(ii) explain the observations in (b) (i) above, (3 marks)
................................
(c) If the experiment was repeated with the Klinostat rotating:
(i) state the observation that was made on the seedlings after three days; (1 mark)
........................
(ii) give a reason for the observation made on the seedlings. (1 mark)
...........................
SECTlON B (40 marks)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8. 6. The graph below shows the relative numbers of three main species of organisms in a pond.
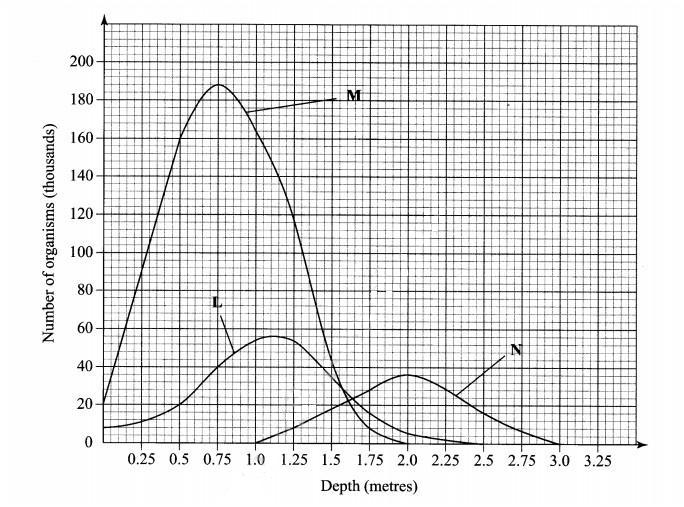
Reason .......................... (1 mark)
(ii) secondary consumer..................... (1 mark)
Reason............................. (1 mark)
(b) State the depths at which each of the populations labelled L, M and N is at its optimum. L .......................................... (1 mark)
M........................................... (l mark)
N........................................... (1 mark)
(c) (i) Which method may have been used to deternine the population of organisms labelled N in the pond? (1 mark)
........................
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (c) (i) above. (1 mark)
........................
(iii) State the assumptions made when using the method in (c) (i) above. (4 marks)
.........................
(d) State two reasons why primary productivity in the pond decreases with depth. (2 marks)
...........................
(e) Explain the ecological importance of fungi to plants. (2 marks)
............................
(f) Why is flooding likely to lead to a cholera outbreak? (3 marks)
.............................
7. Explain the various ways in which seeds and fruits are adapted to dispersal. (20 marks)
............................
8. How is a mammalian heart structurally adapted to its function? (20 marks)
..................................
231/3
BIOLOGY
Paper 3 (PRACTICAL)

2. (a) Animals with wings ...........................................
(b) Animals Without wings.........................................
3. (a) Animals which live in water all the time......................
(b) Animals which live in water some time.........................
4. (a) Animals with scales ..........................................
(b) Animals without scales ......................................
5. (a) Animals with legs ..........................................
(b) Animals without legs ..............................go to 7
6. (a) Animals with six legs ............................ butterfly
(b) Animals with eight legs .....................................
7. (a) Animals with a shell ................................... Snail
(b) Animals without a shell .................................
8. (a) Animals with a jelly-like body ............... ..
(b) Animals without a jelly-like body ..........................
9. (a) Animals with a segmented body ..............................
(b) Animals without a segmented body ...................... Octopus
2.Below are pictures of three mammalian vertebrae
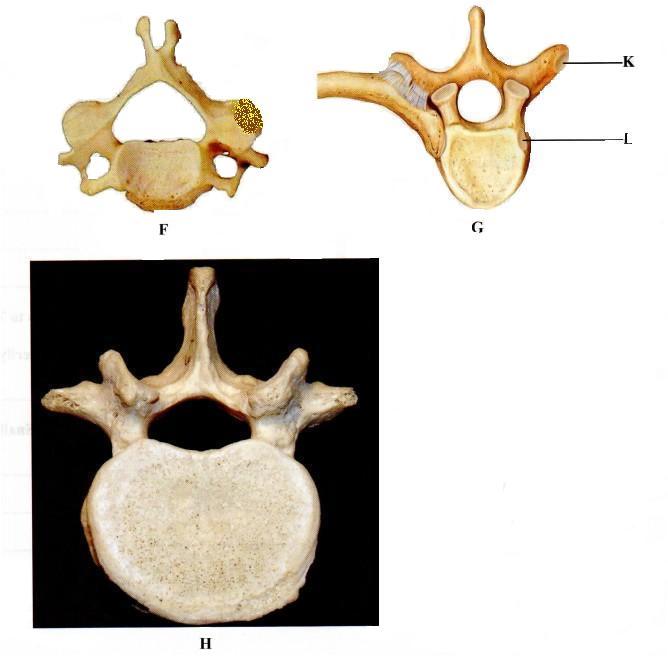
G .......................... (l mark)
H .......................... (1 mark)
(b) Label five parts of the vertebra labelled H. (5 marks)
......................
(c) Name the articular facets labelled K and L.
K .......................... (l mark)
L ......................... (1 mark)
(d) How does each of the parts of a vertebra enable a mammalian skeleton to carry out its functions? (4 marks)
.......................
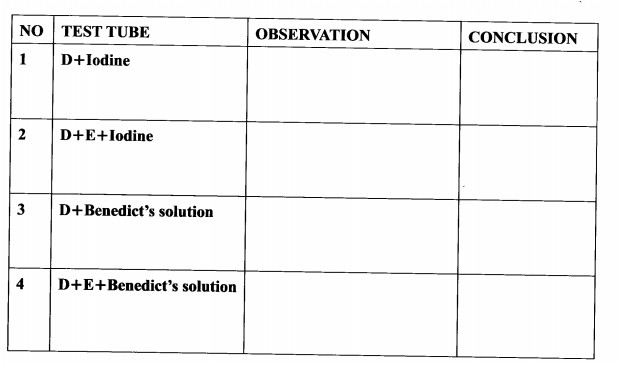
3. You are provided with a 250 ml beaker, four test tubes, solutions labelled D and E, iodine and Benedict’s solutions.
Half fill the beaker with the hot water provided to create a hot water bath.
(I) Label the four test tubes as follows:
(i) test tube 1, D+Iodine
(ii) test tube 2, D+E+lodine
(iii) test tube 3, D+Be|ledict’s solution
(iv) test tube 4, D+E+Benedict’s solufion
(ll) Put 1 cm3 of solution D in each of the four test tubes.
(III) To the D+Iodine test tube, add one drop of iodine solution and shake to mix.
(IV) To the D+E+Iodine test tube, add lcm3 of solution E and two drops of iodine solution. Shake to mix.
(V) To the D+Benedict’s solution test tube, add 1 cm3 of Benedict’s solution and shake to mix.
(VI) To the D+E+Benedict’s solution test tube, add 1cm3 of solution E and l cm3 of Benedict’s solution. Shake to mix.
(VII) Observe the changes in each of the four test tubes.
(VIII) Put all the four test tubes in the hot water bath and observe carefully for about five minutes.
(a) Record the observations and conclusion for each of the four test tubes in the table below.(8 marks)
(i) solution E (1 mark)
...........................
(ii) hot water bath. (1 mark)
.............................
(c) Give the identity of E in human beings. (1 mark)
..............................
(d) Explain the observations made on the reagents tested with Benedict’s solution. (2 marks)
............................
3. CHEMISTRY
CHEMISTRY
Paper 1
(THEORY)
1 (a) Give the name of the first member of the alkene homologous series. (1 mark)
(b) Describe a chemical test that can be used to distinguish butanol from butanoic acid. (2 marks)
2 (a) Name the raw material from which sodium is extracted. (l mark)
(b) Give a reason why sodium is extracted using electrolysis. (1 mark)
(c) Give two uses of sodium metal. (l mark)
3 (a) What is meant by lattice energy? (1 mark)
(b) Study the energy level diagram below and answer the question that follows:
What type of reaction is represented by the diagram? (1 mark)
4 (a) State the Boyles law. (1 mark)
(b)A gas occupies 500 cm3 at 27°C and 100,000 Pa. What will be its volume at 0°C and 101325 Pa? (2 marks)
5 Calculate the mass of Zinc oxide that will‘just neutralise dilute nitric (V) acid containing 12.6 g of nitric (V) acid in water. (Zn = 65.0; O =l6.0, H = 1.0, N = 14.0). (3 marks)
6 Describe how sodium carbonate is used to remove Water hardness. (2 marks)
7 Hydrogen chloride gas can be prepared by reacting sodium chloride with an acid.
(a) Write an equation for the reaction between sodium chloride and the acid. (1 mark)
(b) Give two chemical properties of hydrogen chloride gas. (1 mark)
(c) State two uses of hydrogen chloride. (1 mark)
8 When solid A was heated strongly, it gave off water and a solid residue. When water was added to the solid residue, the original solid A, was formed.
(a) What name is given to the process described? (1 mark)
(b) Give one example of solid A. (1 mark)
9 The set up below was used to investigate the reaction between dry hydrogen gas and copper (II) oxide.
(a) Name substance A. (l mark)
(b) State the observation made in the combustion tube. (1 mark)
(c) Explain the observation stated in (b) above. (1 mark)
10 The atomic number of an element, T is 15.
(a) Write the electronic configuration of the ion T3-. (1 mark)
(b) Write the formula of an oxide of T. (1 mark)
11 Dilute sulphuric (VI) acid was electrolysed using platinum electrodes. Name the product formed at the anode and give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
12 The curve shown below shows the variation of time against temperature for the reaction between sodium thiosulphate and hydrochloric acid.
(a) Write the equation for the reaction between sodium thiosulphate and dilute hydrochloric acid. (1 mark)
(b) Explain the shape of the curve. (2 marks)
13 Dry ammonia and dry oxygen were reacted as shown in the diagram below.
(a) What is the purpose of the glass wool? (1 mark)
(b) What products would be formed if red hot platinum was introduced into a mixture of ammonia and oxygen? (1 mark)
14 The table below shows behaviour of metals R, X, Y and Z. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Arrange the metals in the order of reactivity starting with the most reactive. (2 marks)
(b) Name a metal which is likely to be: (1 mark)
15 Given the following substances: wood ash, lemon juice and sodium chloride.
(a) Name one commercial indicator that can be used to show whether wood ash, lemon juice and sodium chloride are acidic, basic or neutral. (1 mark)
(b) Classify the substances in 15(a) above as acids, bases or neutral. (2 marks)
16 The flow chart below shows various reactions of aluminium metal. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(a) (i) Other than water, name another reagent that could be R. (1 mark)
(ii) Write the formula of reagent Q. (1 mark)
(b) Write an equation for the reaction in step 5. (1 mark)
17 (a) One of the allotropes of sulphur is rhornhic sulphur, name the other allotrope. (1 mark)
(b) Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid reacts with ethanol and copper. State the property of the acid shown in each case. (2 marks)
18 Study the standard electrode potentials in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Which of the metals is the strongest reducing agent? (1 mark)
(b) What observations will be made if a silver coin was dropped into an aqueous solution of copper (II) sulphate? Explain. (2 marks)
19 A radioactive substance weighing M kg took 1900 years for the original mass to reduce to l5 kg. Given that the half life of the radioactive substance is 380 years;
(a) Determine the original mass of the radioactive substance. (2 marks)
(b) State two uses of radioactivity in medicine. (1 mark)
20 A crystal of iodine, heated gently in a test tube gave off a purple vapour.
(a) Write the formula of the substance responsible for the purple vapour. (1 mark)
(b) What type of bond is broken when the iodine crystal is heated gently? (1 mark)
(e) State one use of iodine. (1 mark)
21 Describe how samples of lead (II) sulphate, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride can be obtained from a mixture of the three. (3 marks)
22 Study the flow chart below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name process T
(b) Give the formula of W.
(c) State two uses of X.
23 The table below is part of the periodic table. The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Select an element which is stored in paraffin in the laboratory. (l mark)
(b) How do the ionic radii of E and I compare? Explain. (2 marks)
24 The graph below is a cooling curve for water. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Explain what happens to the molecules of water in the region BC in terms of kinetic theory. (2 marks)
(b) In what state is the water in the region DE? (1 mark)
25 Starting with barium nitrate solution, describe how a pure sample of barium carbonate can be prepared in the laboratory. (3 marks)
26 A hydrocarbon contains 14.5% of hydrogen. If the molar mass of the hydrocarbon is 56, determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon. (C = 12.0; H = 1.0) < (3 marks)
27 (a)Describe how carbon (IV) oxide can be distinguished from Carbon II Oxide using calcium hydroxide solution. (2 marks)
(b)What is the role of carbon (IV) oxide in fire extinguishing? (l mark)
28 (a)State one source of alkanes. (1 mark) (b)Ethane gas was reacted with 1 mole of bromine gas. State one observation made during this reaction. (1 mark)
29 An electric current was passed through several substances and the results obtained recorded in the table below.
Which of these substances is likely to be: (a) magnesium (1 mark)
(b) hexane (1 mark)
(c) lead (II) bromide (1 mark)
CHEMISTRY
Paper 2
(THEORY)
1 (a) (i) Carbon (IV) oxide is present in soft drinks. State two roles of carbon (IV) oxide in soft drinks. (l mark)
(ii) Explain the observation made when a bottle containing a soft drink is opened. (2 marks) ;
(iii) Carbon (IV) oxide dissolves slightly in water to give an acidic solution. Give the formula of the acid. (1 mark)
(b) Zinc oxide can be obtained by heating zinc nitrate. A student healed 5.76 g of zinc nitrate.
(i) Write an equation for the reaction that occurred. (1 mark)
(ii) Calculate the total volume of gases produced. (Molar gas volume is 24 dm3; Zn = 65.4; O = 16.0; N = 14.0). (4 marks)
(iii) Identify the element that is reduced when zinc nitrate is heated. Give a reason. (2 marks)
2 (a) Draw the structure of the following compounds. (2 marks)
(i) Butanoic acid;
(ii) Pent-2-cue.
(b) Explain why propan-l-ol is soluble in water While prop-1-ene is not. (Relative molecular mass of propan-1-ol is 60 while that of prop-1-ene is 42). (2 marks)
(c) What would be observed if a few drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) were added to oil obtained from nut seeds? Explain. (2 marks)
(d) State one method that can be used ‘to convert liquid oil from nut seeds into solid. (1 mark)
(e) Describe how soap is manufactured from liquid oil from nut seeds. (3 marks)
(f) 0.44 g of an ester A reacts with 62.5 cm3 of 0.08 M potassium hydroxide giving an alcohol B and substance C. Given that one mole of the ester reacts with one mole of the alkali, calculate the relative molecular mass of the ester. (2 marks)
3 (a)Name the method that can be used to obtain pure iron (Ill) chloride from a mixture of iron (III) chloride and sodium chloride. (1 mark)
(b) A student was provided with a mixture of sunflower flour, common salt and a red dye. The characteristics of the three substances in the mixture are given in the table below.
The student was provided with ethanol and any other materials needed.
Describe how the student can separate the mixture into its three components. (3 marks)
(c) The diagram below shows part of a periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements. Use the diagram to answer the questions that follow.
(i) Explain why the oxidising power of W is more than that of X. (2 marks)
(ii) How do the melting points of R and T compare? Explain. (2 marks)
(iii) Select an element that could be used:
(I) in Weather balloons; (1 mark)
(II) for making a cooking pot. (l mark)
(d) (i) Classify the substances water, iodine, diamond and candle wax into elements and compounds. (2 marks)
(ii) Give one use of diamond. (1 mark)
(a) The diagram below represents a dry cell. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
(i) Which of the letters represent:
(I) carbon electrode? (1 mark)
(II) the electrolyte? (1 mark)
(ii) One of the substances used in a dry cell is manganese (IV) oxide. State two roles of manganese (IV) oxide in the dry cell. (2 marks)
(b) Below is a simplified electrolytic cell used for purification of copper. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
(i) Identify the cathode. (1 mark)
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction at the anode. (1 mark)
(iii) What name is given to L? (1 mark)
(iv) A current of 0.6 A was passed through the electrolyte for 2 hours. Determine the amount of copper deposited. (Cu = 63.5; l Faraday = 96,500 coulombs). (3 marks)
(v) State two uses of copper metal. (1 mark)
5 The set-up below can be used to generate a gas without heating. This occurs when substance M reacts with solid N.
(a) (i) Complete the table below gluing the names of substance M and solid N if the gasses generated are chlorine and sulphur (IV) oxide. (2 marks)
(ii) Complete the diagram above to show how a dry sample of sulphur (IV) oxide can be collected. (3 marks)
(b) Describe two chemical methods that can be used to test the presence of sulphur (IV) oxide. (3 marks)
(c) Other than the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid, state two uses of sulphur (IV) oxide. (2 marks)
6 (a) Other than concentration, state two factors that determine the rate of a reaction.(2 marks)
(b) In an experiment to determine the rate of reaction, excess lambs of calcium carbonate were added to 2 M hydrochloric acid. The mass of calcium carbonate left was recorded after every 30 seconds. The results are shown in the table below.
(i) Write the equation for the reaction that took place. (1 mark)
(ii) On the grid provided, plot a graph of mass of calcium carbonate vertical axis against time. (3 marks)
(iii) Determine the rate of reaction at the 105th second. (3 marks)
(c) Why does the curve level off after some time? (1 mark)
(d) On the same grid, sketch a curve for the same reaction using 4 M hydrochloric acid and label the curve R. (2 marks)
7 (a)Naturally occurring magnesium consists of three isotopes. 78.6% 24Mg; 10% 25Mg and 26Mg. Calculate to one decimal place, the relative atomic mass of magnesium. (2 marks)
(b) When magnesium burns in air, it forms a white solid and a grey-green solid. When a few drops of water are added to the mixture, a gas that turns red litmus paper blue is evolved.
Identify the:
(i) White solid. (1 mark)
(ii) gas evolved and state its use.
(I) Name of gas. (1 mark)
(II) Use of the gas. (1 mark)
(c) Two different samples of water (I and II) were tested with soap solution. Sample II was further subjected to two other processes before adding soap. 20 cm3 of each sample of water was shaken with soap solution in a boiling tube until a permanent lather was obtained. The results are shown in the table below.
(i) Identify the water sample that had temporary hardness. Explain your answer.(2 marks)
(ii) Explain why the results for sample II are different after distilling but remain unchanged after filtering. (2 marks)
(m) State two disadvantages of using both water samples for domestic purposes. (2 marks)
CHEMISTRY
Paper 3
(PRACTICAL)
1. You are provided with:
- 2.0 g of substance A, labelled solid A.
- Solution B, 0.05 M hydrochloric acid.
- Methyl orange indicator.
You are required to determine the:
- solubility of substance A in water.
- relative formula mass of substance A.
PROCEDURE I
(i)Place 200 cm’ of. tap water in a 250 ml beaker and keep it for use in step (vi).
(ii)Place all of substance A in a dry boiling tube.
(iii)Using a burette, measure 10.0 cm3 of distilled water and add it to the substance A in the boiling tube.
(iv)While stirring the mixture in the boiling tube with a thermometer, warm the mixture using a Bunsen burner, until the temperature rises to 65°C. Stop warming the mixture.
(v)Allow it to cool while stirring with the thermometer.
(vi)When the temperature drops to 60°C, start the stop watch/clock, place the boiling tube in the beaker with tap water prepared in step (i) above.
(vii)Continue stirring and record the temperature of the mixture after two minutes, then thereafter record the temperature of the mixture after every one minute interval and complete table 1. Retain the mixture with the thermometer inside for use in procedure II below.
(4 marks)
On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature (vertical -axis) against time. (3 marks)
(a) Using the graph, determine the temperature (Ts) when 2.0 g of substance A dissolves completely in 10.0 cm3 of distilled water. (1 mark)
(b) Calculate the solubility of substance A in grams per 100 g water at temperature, Ts. (2 marks)
PROCEDURE II
Using a funnel, transfer all the mixture obtained from Procedure I into a 250 ml volumetric flask. Rinse the boiling tube and the thermometer with about 20 cm3 of distilled water and add the rinses into the volumetric flask. Repeat the rinsing two more times. Add about 100 cm3 of distilled water to the volumetric flask. Shake until all the solid dissolves. Add more distilled water to the mark. Label this as solution A. Fill the burette with solution A. Using a pipette and pipette filler, place 25.0 cm3 of solution B, into a 250 ml conical flask. Add three (3) drops of the indicator provided and titrate using solution A. Record your readings in table 2 below. Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table.
(3 marks)
(a) Calculate the:
(i) average volume of solution A used. (1 mark)
(ii) number of moles of hydrochloric acid, solution B used. (l mark)
(b) Given that two moles of acid react with one mole of substance A, calculate:
(i) number of moles substance A used. (1 mark)
(ii) concentration of solution A in moles per litre; (1 mark)
(iii) concentration of solution A in g per litre; (l mark)
(iv) relative formula mass of substance A. (1 mark)
2. You are provided with solid C. Carry out the following tests and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided. Place all the solid C in a boiling tube. Add about 15 cm3 of distilled Water and shake until all the solid dissolves. Use 2cm3 portions of the Sodium solution in a test tube, for each of the tests in (a), (b), (c), (d), (e) and (f).
3 You are provided with substance L. Carry out the following tests and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided. Use about 2 cm3 portions of substance L in a test-tube for each of the tests, (a), (b), (c) and (d).
